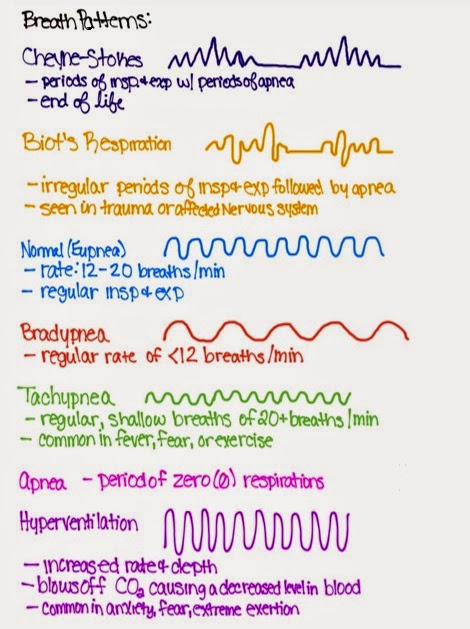
Breath patterns are extremely important to notice while assessing a patient as a nurse.
Here are the most common ones that you should know:
Cheyne-Stokes Respiraton
Often found when a person is at the end of their life, however, it is common in infants and elderly while they are asleep. They have regular periods of inspiration and expiration followed by period of apnea.
Biot's Respiraton
Irregular patterns of inspiration, expiration, and apnea. Often found in patients who have had severe trauma to the head or any severe problems with the nervous system (spinal cord or brain).
Eupnea (Normal)
Regular and constant cycle of inspiration and expiration. There are no periods of apnea. The rate is 12-20 breaths/minute.
Bradypnea
Regular breaths at a lower rate than eupnea (<12 breaths/minute).
Tachypnea
Increased rate of regular, shallow breaths (20+ breaths/minute). Often found in those experiencing fear, have a fever, or recently exercised.
Hyperventilation
Increased rapid rate of regular deep breaths that occur in patient's who are experiencing fear, anxiety, or extreme exertion. Hyperventilation is when the person believes that they are not receiving enough oxygen, when in fact, they are over-oxygenating and there is a lack of carbon dioxide in their blood system.